Mesolithic Age: Food, Cloths, & Tools.
Mesolithic Age: New Phase of Human Adaptation in the Ancient Era.
The Mesolithic Age spanned about 10,000 to 5,000 BCE. It was a time of change between the Paleolithic and Neolithic eras.The Mesolithic Age began when the environment shifted. This shift followed the end of the last Ice Age around 10,000 BCE. As glaciers retreated, landscapes underwent significant changes, giving rise to diverse ecosystems and prompting shifts in human adaptation strategies.As glaciers retreated, landscapes changed a lot. This created new ecosystems and led to shifts in how humans adapted. The warming climate helped new plants and animals emerge, the Mesolithic Age Around 9000 BCE the climate of the earth became warm and dry as a result ice age came to an end. In 9000 BCE an intermediate stage began in Stone Age culture. It is termed as Mesolithic age. was a transitional phase between the Palaeolithic and Neolithic age. The term Mesolithic is derived from the two Greek words Meso and lithic meaning middle Stone Age. During this period man made some improvements in almost every aspect of life. Mesolithic occupations were hunting, fishing, and food gathering. At a later stage, they started domesticating animals and used to live on small hillocks.The sites of the Mesolithic age were in Rajasthan, Gujarat, Kutch, Punjab, and central and eastern India. They were also in the south of the Krishna River. Bagor in Rajasthan is well excavated. The earlier evidences of domestication of animals around 5000 BCE is found at Adamgarh in M.P. and Bogar in Rajasthan.
 |
| In India Krishna River was sacred area for living because Water was very close to use |
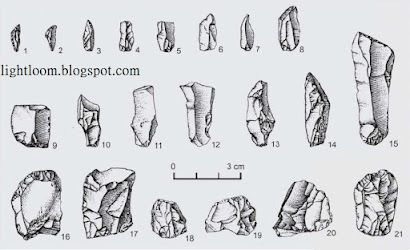
Many improvements also were noticed in this age especially in weaponry. Weapons were made of animal bones. Besides man had started making weapons with jasper, chert. The weapons of this age were extremely small. They were, therefore, know as Microliths or pygmy tools. They were used by a wooden handle on their one side. The people of Paleolithic and Mesolithic ages practiced painting. Rock shelters, Bamboo brushes were used to draw figures of birds, animals, human beings and mostly red-pigments were used. These paintings represent hunting scenes, drawing of animals and hieroglyphics. The social organization in this period tended to become more stable than that of Paleolithic age. The extent of the Mesolithic age was 9000-4000 BCE.
There is no doubt in that it paved the way for the rise of the Neolithic culture. Mesolithic communities got most of their food from the natural environment. Nomadic hunter-gatherer lifestyles prevailed during this era, and these societies depended heavily on diverse resources for their survival. People lived as nomadic hunter-gatherers during this era. They depended heavily on diverse resources for survival, Hunting was crucial.
Hunting:
In the Mesolithic Age, hunting was vital for nomads. It was their way of getting food. Hunter-gatherer societies relied on specialized tools such as microliths and harpoons to pursue game animals and fish. This hunting prowess was essential for survival, providing meat, bones, and hides for clothing, reflecting the resourcefulness of Mesolithic peoples in adapting to their environments.
Cloths:
Cloths In the Mesolithic Age, people crafted clothing from materials found in the environment. Nomadic hunter-gatherer communities used animal hides and furs obtained through hunting for warmth and protection. Nomadic hunter-gatherer communities used animal hides and furs obtained through hunting for warmth and protection. These garments were fashioned with primitive tools. They showed the resourcefulness of Mesolithic people. They adapted to climate and used nature for basic clothing.
Tools:
During the Mesolithic Age, communities developed specialized tools, notably microliths. These small, well-made stone tools served many purposes. They made hunting, cutting, and processing resources easier. Microliths exemplified technological advancements, reflecting the resourcefulness of Mesolithic societies in adapting tools to their dynamic environments.
Food:
Mesolithic communities relied on a diverse diet obtained through hunting, fishing, and gathering.Hunting provided meat, bones, and hides, while fishing contributed to their protein intake. Gathering involved collecting wild fruits, nuts, seeds, and edible plants. It ensured a balanced and varied diet.
 |
| Food of Mesolithic Age almost Fishes, and wild Animals. |







Nice
ReplyDelete